Patient EducationOur mission is to help you be more medically prepared. Stay up-to-date on the latest news in health and preparedness.Categories
How do Antibiotics Work? Part 4

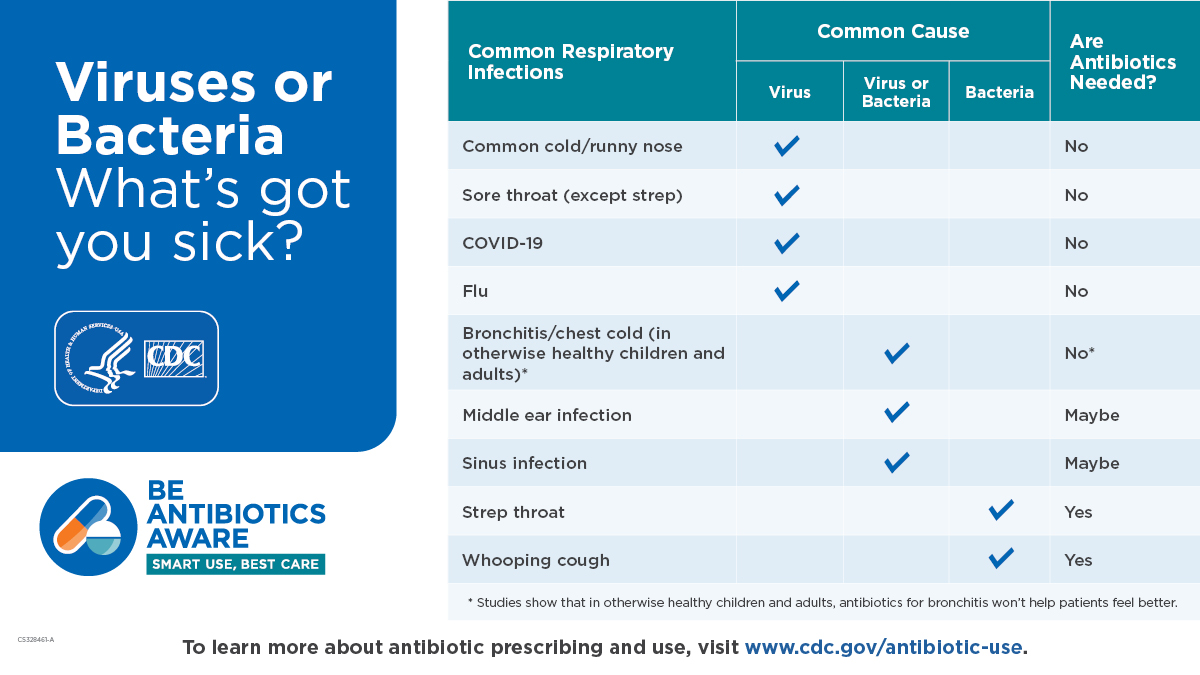
The best way to take antibiotics is to never need them. But that isn’t always an option. However, there are some steps you can take to strengthen your immune system so that you and your loved ones can fight off illness. The recent outbreak of deaths from group A strep– which is usually treated with Amoxicillin, is currently in short supply. This highlights the fragility of our nations drug supply. Check this site for current drug shortages- if a medication you are taking is on the list contact your care provider to get your medications refilled, and if available ask for a years supply of your meds.
8 tips to strengthen your immune system
- Get good quality sleep
According to the Sleep foundation good quality sleep enhances both the innate and adaptive immune system responses. Non rapid eye movement, known as NREM is deep sleep slows the body’s processes allowing more energy to be directed at healing. Sleep is such an important topic that it really needs its own post.
- Cut back on sugar
Professor of immunobiology at Yale, Ruslan Medzhitov performed experiments on mice- after infecting the mice with the bacteria Listeria monocytogenes he fed one group fat and proteins. They lived. The group he fed simple carbohydrates died. Conversely, when the mice were infected with an influenzas virus and fed fats and proteins, they were more likely to die compared to the mice fed simple carbohydrates. In other words, balance is the key. If unsure if you have a viral or bacterial infection it is best to just cut out excess sugar.
- Increase fresh fruits and vegetables
Up to 80% of our immune system is housed in lymphoid tissue in your intestines, It is called gut associated lymph tissue (GALT) By eating fiber rich foods the beneficial bacteria help the immune system do its job. In addition, a study found that eating a diverse diet high in fiber rich foods can help combat antibiotic resistance. There needs to be more research in this area of study, however initial results are promising.
In addition, several varieties of mushrooms are known to improve immune system function and are being studied for their cancer fighting properties.
- Drink plenty of water
Water helps flush toxins out of the body, both through elimination and mucus membranes.
The bloodstream is comprised mostly of water. To help the body fight infection keeping hydrated helps the white blood cells do their job- fight infections.
Both can decrease immunity
- Keep your vitamin D levels up
Vitamin D is well known to help fight infections. Be sure that when you take vitamin D (which is really not a vitamin, it is a steroid hormone) be sure to add vitamin K2, also known as MK 7, This is important, because this helps avoid calcium buildup in your arteries.
- Reduce and manage stress
Stress raises our cortisol levels which in turn suppresses the immune response to pathogenic invaders.
- Exercise to boost immunity
Research shows that 20–40 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day is adequate to provide a positive boost to the immune system. Exercise helps circulate the infection fighting cells in the body.
If you still need an antibiotic Jase has you covered
The 5 antibiotics in the Jase case can cover a wide range of bacterial illnesses. If in doubt contact Jase provider for guidance, part of the outstanding service Jase offers is unlimited follow up for questions about antibiotic use.
Let’s take a look at some of the infections Jase antibiotics cover:
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg tablets (28 tablets)
When amoxicillin is not available due to current shortages this antibiotic can be substituted. Other uses include group A strep, sinusitis, pneumonia, ear infections, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and infections of the skin
- Azithromycin 250 mg tablets (6 tablets)
Bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, skin infections, Travelers diarrhea, urinary tract infection
- Ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablets (28 tablets)
Bioterrorism infections from anthrax, Tularemia or plague exposure
Travelers diarrhea
- Doxycycline 100 mg capsules (120 capsules)
Bioterrorism infections from anthrax, Tularemia, or plague exposure
Skin infection, tetanus, bites (animal or human)
- Metronidazole 500 mg tablets (30 tablets)
bacterial vaginosis, diarrhea (caused by giardia and clostridioides difficile), giardiasis, tetanus, and trichomoniasis
- Brooke Lounsbury
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Blog
The Silent Killer (Part 2)
(Part 2) Part 2 will discuss: Physiology of blood pressure regulation, Medications to help control hypertension Blood pressure regulation is a complex process involving a series of body systems, hormones and input from the nervous system all working together to...
The Silent Killer
Part 1 High blood pressure (HBP) has been called the silent killer and with good reason. It is estimated that at least 20 percent of the population with high blood pressure have no symptoms. In part 1 we will discuss: Symptoms of hypertension Health risks of...